Before you start monitoring video in Security
Desk, you should decide how you want to
use each video stream, and configure the appropriate settings for it.
What you should know
Every video stream setting affects your bandwidth and archive storage. You must find a
balance between quality, CPU usage, and disk space.Security
Desk only switches to a higher resolution
when it makes a visual difference to the users. Therefore, make sure the Live stream
has a better resolution than the Low resolution stream, and that the High
resolution stream has a better resolution than the Live stream.
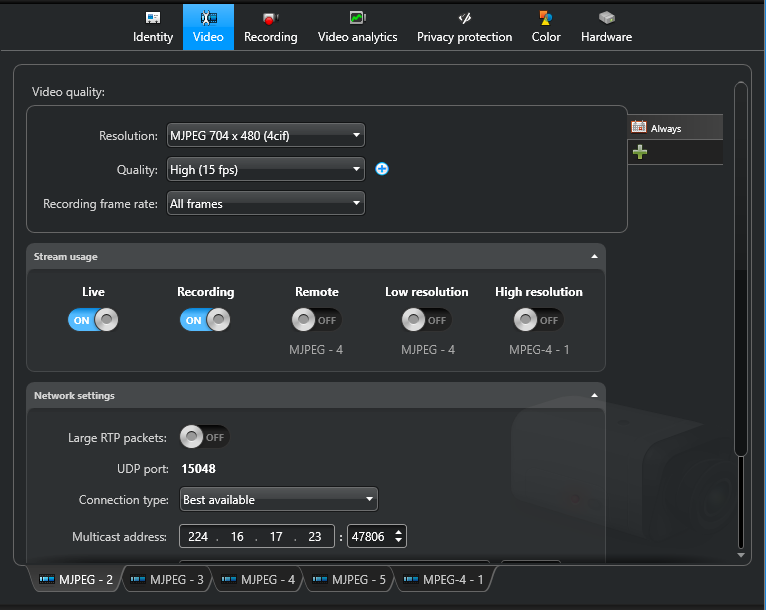
To configure a camera’s video streams:
-
From the Config
Tool home page, open the
Video task.
-
Select the camera to configure, and then click the Video
tab.
-
If the camera supports multiple video streams, select a video stream tab at the bottom
of the Video tab.
-
In the Video quality section, set the video quality settings
(resolution, frame rate, and so on) for the selected video stream.
-
In the Stream usage section, specify the purpose for the
selected video stream.
NOTE: A stream can be assigned all, some, or none of the usage options. A
stream that has no usage assigned is not generated by the video encoder, which conserves
CPU on the unit.
Live:

Default stream used for viewing live video in Security
Desk.
Recording:

Stream recorded by the Archiver for future investigation.
TIP: The
quality of the recording stream can be temporarily boosted when the recording is
triggered by certain types of events.
Remote:

Stream used for viewing live video when the bandwidth is limited.
Low resolution:

Stream used instead of the Live stream when the tile used to view the
stream in Security
Desk is small.
High resolution:

Stream used instead of the Live stream when the tile used to view the
stream in Security
Desk is large.
-
In the Network settings section, click Connection
type and select how communication between the Archiver and the camera is
established for sending or receiving video streams:
Best available:

Lets the Archiver select the best available connection type for the stream. The
best available types rank in this order, according to availability:
- Multicast (not available for the recording stream).
- UDP
- TCP
- RTSP over HTTP
- RTSP over TCP
Unicast UDP:

Forces the stream to be sent in UDP to the Archiver. The stream must be formatted
using the RTP protocol.
Unicast TCP:

Forces the stream to be sent in TCP to the Archiver. Here, TCP is taken in the
broad sense. For some types of cameras, the Archiver establishes a TCP connection to
the unit and receives the stream in a proprietary protocol. For others, the stream
is sent over HTTP. Typically, the stream is not formatted according to the RTP
protocol by the unit. The Archiver has to convert the stream to the RTP protocol to
be archived or retransmitted to the system.
RTSP stream over HTTP:

This is a special case of TCP connection. The Archiver uses the RTSP protocol to
request the stream through an HTTP tunnel. The stream is sent back through this
tunnel using the RTP protocol. This connection type is used to minimize the number
of ports needed to communicate with a unit. It is usually the best way to request
the stream when the unit is behind a NAT or firewall, because requests sent to HTTP
ports are easily redirected through them.
RTSP stream over TCP:

This is another special case of TCP connection. The Archiver uses the RTSP
protocol to request the stream in TCP. The request is sent to the RTSP port of the
unit.
-
Click Apply.
-
Configure the other video streams available on the camera.